Document Object Model
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for web documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content. The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects. That way, programming languages can interact with the page.
The DOM consists of:
- The entire document as a node.
- Elements in the document, which can contain other elements and nodes.
- HTML attributes as nodes.
- Text within HTML elements as nodes.
- Comments in the document as nodes.
The DOM provides methods and properties to access and manipulate nodes and elements. For example, you can use the getElementById() method to get an element by its ID attribute, and then use the innerHTML property to change the text content of the element.
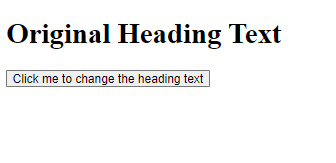
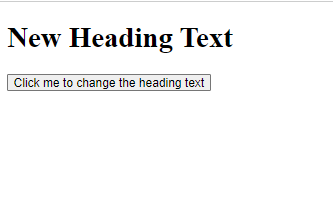
Example :<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>DOM Example</title> <script> function changeText() { var heading = document.getElementById("myHeading"); heading.innerHTML = "New Heading Text"; } </script> </head> <body> <h1 id="myHeading">Original Heading Text</h1> <button onclick="changeText()">Click me to change the heading text</button> </body> </html>
Output :
Explanation :
In this example, we have an HTML document with a heading element and a button element. The changeText() function uses the getElementById() method to get the heading element by its ID, and then changes its innerHTML property to update the text content.When the button is clicked, the changeText() function is called and the heading text is updated to “New Heading Text”.









No Comment! Be the first one.